
/GettyImages-141527436-56aaeabb5f9b58b7d009182d.jpg)
Freemont, John Denton, in Diagnostic Cytopathology (Third Edition), 2010 Gross analysisīecause synovial fluids from inflamed joints have a tendency to clot, they should be received in the laboratory in anticoagulant. Results appear promising for the diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection in sonication and synovial fluid as well as septic arthritis in synovial fluid of native joints.Īnthony J. The advantage of automated multiplex PCR (MPCR) lies in the rapid identification of causative pathogens and their antibiotic sensitivities (5 hours compared with several days in standard tissue culture techniques). Molecular methods such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technique are used to identify bacteria by their genotypes. Studies are being conducted to develop tests for rapid and accurate diagnosis of septic arthritis. The use of empirical antibiotics may obscure results.

Cultures can be negative in up to 75% of patients with septic arthritis. Combining standard joint fluid markers with the absence of microcrystals improves diagnosis of septic arthritis compared to standard cytologic features used alone.Īlthough synovial fluid culture is useful in the diagnosis of septic arthritis, both false negatives and false positives can occur. Furthermore, infection developing concomitantly with crystal-induced arthritis may be overlooked when the joint fluid examination shows microcrystals. In addition to the total leukocyte count, the proportion of polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs), if greater than 90%, indicates infection.Ĭrystal-induced arthritis is the main differential diagnosis in septic arthritis, as the clinical manifestations may be similar and the joint fluid findings comparable. However, features classically taken to indicate septic arthritis include cloudy or turbid joint fluid, a nucleate cell count greater than 50,000/mm, or a high percentage of neutrophils leukocyte counts of 28,000/mm or less also have been implicated, especially in immunocompromised patients. A leukocyte count greater than 2000/mm 3 points toward inflammation, whereas lower counts suggest a mechanical disorder. A C-reactive protein of more than 10.5 mg/dL is predictive of infection. Measuring erythrocyte sedimentation rates or C-reactive protein levels may be helpful in following the treatment course. The synovial fluid obtained should be sent for immediate Gram staining, culture, cell counts, and crystal analysis. The current benchmark for identification of the causative microorganism and ascertaining its antimicrobial susceptibility is the conventional culture of aspirated joint fluid.
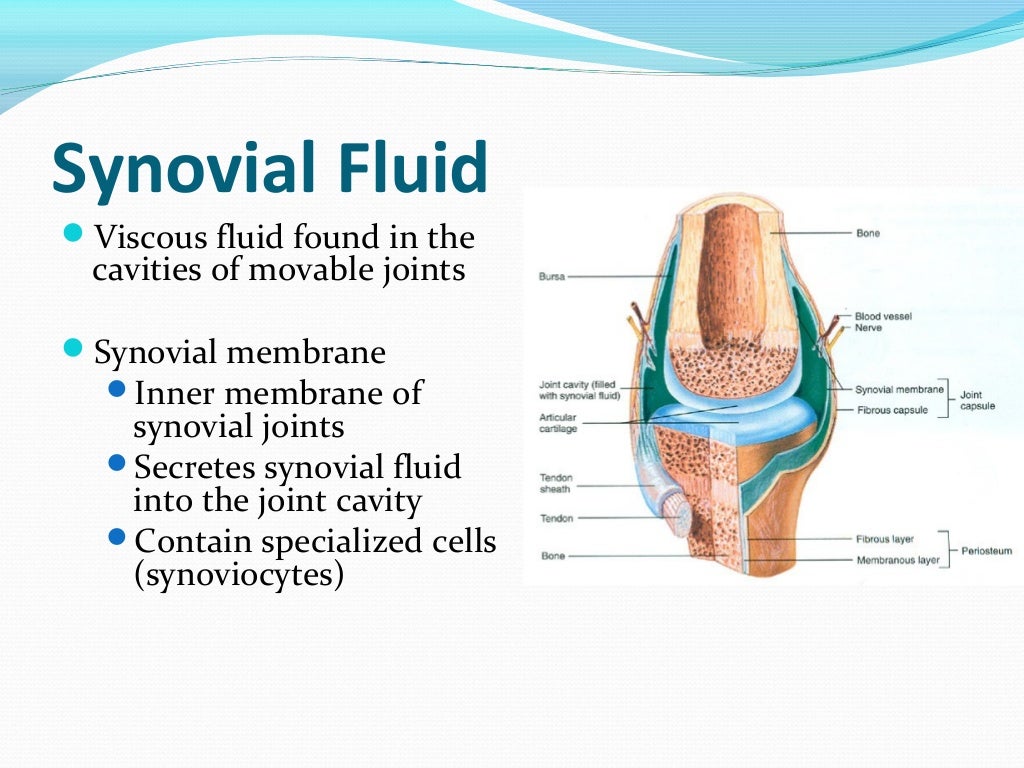
Therefore, early diagnosis is the most important factor for functional prognosis in patients with septic arthritis. An estimated 25% to 50% of patients with septic arthritis end up with irreversible loss of joint function. The organisms and/or the cytotoxins they may produce can irreversibly damage cartilage and subchondral bone within only a few days. The importance of early diagnosis and treatment of septic arthritis prior to destruction of an affected joint is well established. Azar MD, in Campbell's Operative Orthopaedics, 2021 Synovial Fluid Studies


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
